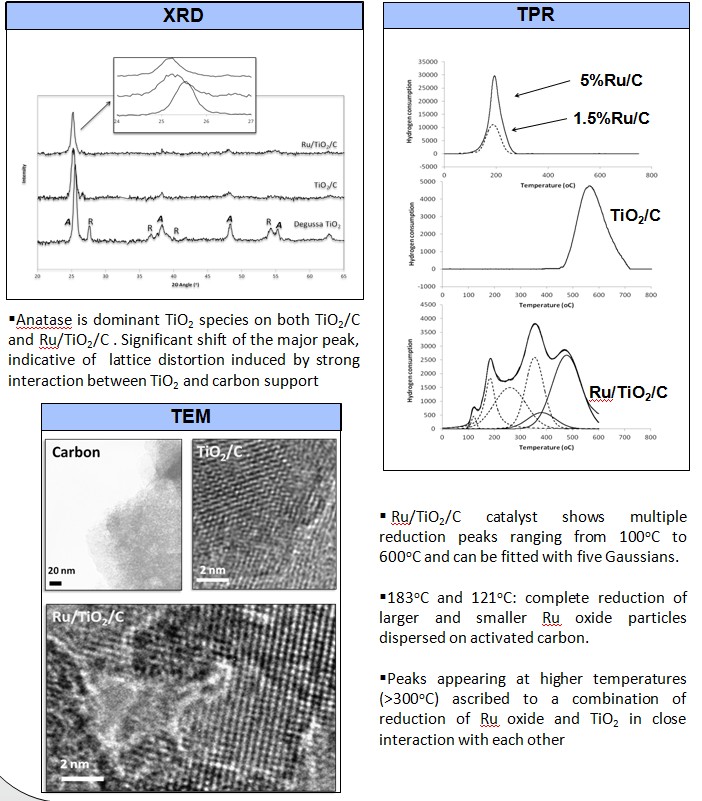
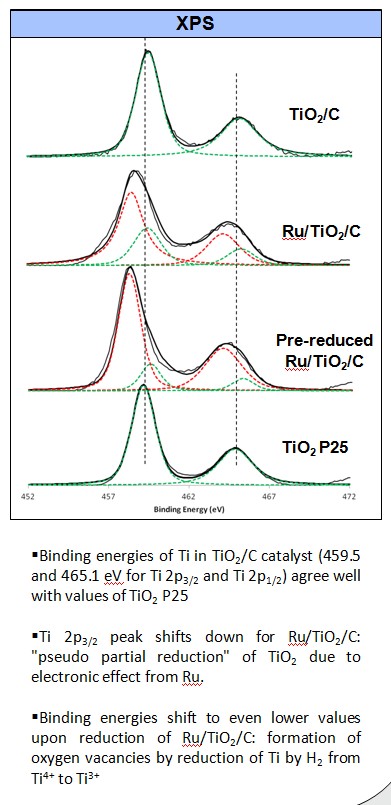
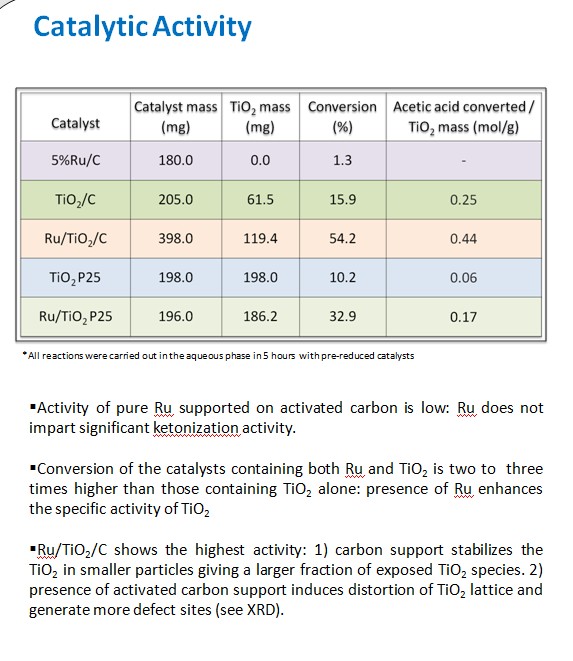
Ketonization of acetic acid in the liquid phase using TiO2/C and Ru/TiO2/C catalysts have been investigated. High surface area of activated carbon can enhance the dispersion of TiO2 particles, and increase the adsorption of acetic acid in water. In addition, the hydrophobicity of the carbon support can impede the interaction between the active species and water molecules, even in aqueous media. On the other hand, Ru significantly improves the reducibility of TiO2, creates more oxygen vacancies, and consequently its ketonization activity.
The results reported here indicate that the combination of Ru, TiO2, and activated carbon (Ru/TiO2/C) creates a unique catalyst system with potential for reactions in hot liquid acids. Several characterization techniques were employed (XPS, TPR, TEM) to investigate the interactions of the three components. They provide fairly detailed information about the structure and functionality of this catalyst.