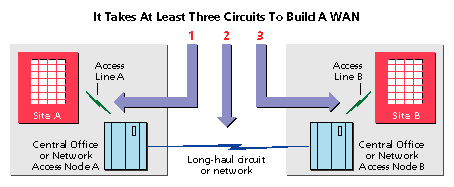
No matter what WAN service you choose-frame relay, SMDS, leased lines or the Internet-an end-to-end link is created via three essential components: From each site, an access line must be run to the local exchange carrier (LEC) or competitive access provider (CAP) serving the area. The third component sits in the middle, joining the two access points. This is the portion supplied by the frame relay backbone.

Nearly all landline-based communications are built this way, because of the structure put in place shortly before the divestiture of AT&T in the early 1980s, when the domestic United States was broken into 160 Local Access Transport Areas (LATAs). A central office (CO) serves a LATA, and links between LATAs must be provided by an interexchange service, even if they sit right next to each other.
While the Telecommunications Act of 1996 reformed some of these rules, major changes to the structure have been slow in coming. So we're still dealing with two or three carriers for a given point-to-point link. Coordinating the services of these vendors can be so time-consuming that there are now a large number of third parties whose main business is to help you manage these vendors.
Local loop fees may have many components, such as carrier interconnection charges and coordination fees. For simplicity, local loop fees in our examples are assumed to include these miscellaneous charges.
For connections to your nearest CO, you have a few options.
Accessing the network is a significant cost item, and you don't have many options. Fortunately, access lines can be shared when using frame relay.
| 56 Kbps Dedicated | 56 Kbps | fixed | Majority of access lines are of this type. Typically 20 percent to 25 percent the cost of T1 service |
| ISDN BRI (typical) | 128 Kbps | fixed + usage | Mainly used for dialup (non-LAN) connections to preconfigured PVC |
| Fractional T1 | 56 Kbps to 1,536 Kpbs | fixed | Requires T1 to end site. Unused T1 channels can be used for other services |
| T1 | 1536 Kbps | fixed | Current maximum rate for most frame relay networks |
Once connected to the local CO, you have many more networking
alternatives. As noted earlier, frame relay competes with a number
of services for the long haul dollar, and can save a lot of money
in the right environment.