|
|
Experiment Design December, 2005 Manuscript Microarray Data
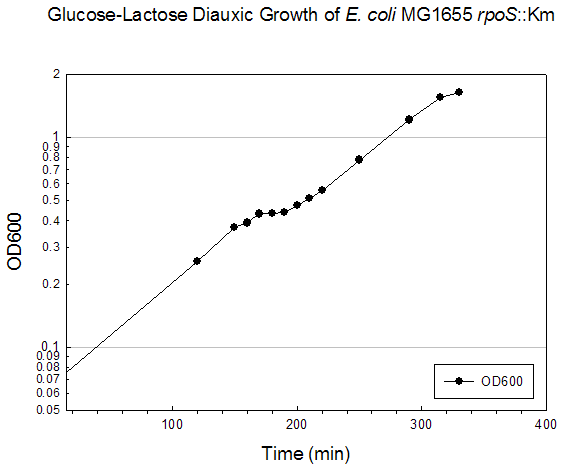
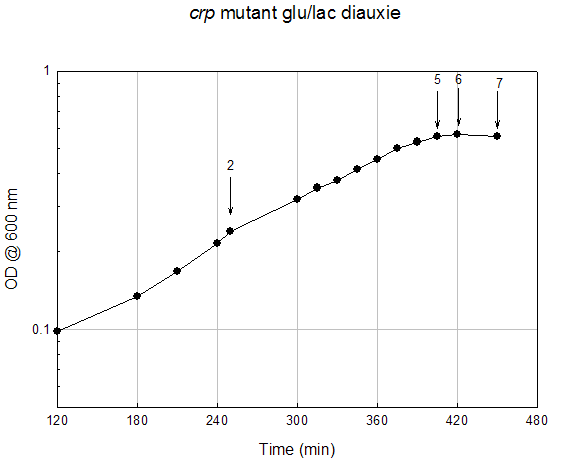
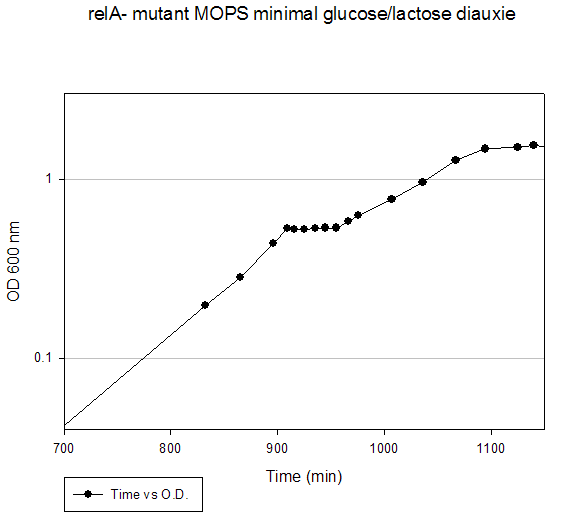
Growth Data Sets Project summary. When cultured on a mixture of glucose and lactose, E. coli grows preferentially on glucose until it is exhausted, resulting in growth arrest while the cells adjust to growth on lactose, i.e., diauxie. K-means clustering of the transcriptome dataset of wildtype E. coli during glucose-lactose diauxie revealed three regulatory networks (RpoS, Crp, and RelA) that dominated the transcription profile. Therefore, we investigated the temporal changes in transcription during glucose-lactose diauxie in the wildtype and mutants lacking the key regulators, RpoS, Crp, and RelA (ppGpp synthetase). Strains and growth conditions. E. coli MG1655 and isogenic mutants were cultured in a 2 l Biostat B fermentor (B. Braun Biotech International) containing 1 liter of Morpholinepropanesulfonic acid (MOPS) minimal medium with 0.5 g/l of glucose and 1.5 g/l of lactose, as described (3) . The temperature was maintained at 37 ºC and pH was kept constant at 7.2 by the addition of 2 M NaOH. The dissolved oxygen level was maintained above 20% of saturation by adjusting the agitation speeds in the range of 270-500 rpm with fixed 1 l/min air flow. Growth was monitored as absorbance at 600nm. E. coli D relA 251::kan R was a gift from M. Cashel, constructed as described (14) . The E. coli D crp ::kan R and D rpoS ::kan R strains were constructed by allelic replacement (15) of the entire genes. These mutant strains are isogenic with E. coli MG1655. Microarray analysis. Microarray analysis was carried out essentially as described (16) . Total RNA was extracted from cells, diluted (1:1) in ice-cold RNAlater (Ambion) and purified using RNeasy columns (Qiagen), as described (3) . RNA was labeled by first strand cDNA synthesis using reverse transcriptase, random primers, and aminoallyl-dUTP incorporation; Cy-3 and Cy-5 dyes were chemically coupled in vitro to the aminoallyl-derivatized cDNA. The oligonucleotide microarrays used in this study were printed on GAPS II slides (Corning) with a probe set containing 70 base oligonucleotide probes for all E. coli MG1655 genes (Operon Biotechnologies) using a Molecular Dynamics Gen III Array Spotter (Amersham Biosciences). Slides were hydrated and flash-dried, UV-cross-linked, and blocked with succinic anhydride, then equal amounts of the Cy-3 and Cy-5 labeled samples were hybridized in triplicate to microarrays using a Discovery system and ChipMap reagents (Ventana Medical Systems). For all microarrays, the experimental sample was labeled with Cy-5 and the control, from early logarithmic growth of E. coli MG1655 wildtype on minimal glucose medium, was labeled with Cy-3. Hybridized slides were scanned on a GenePix4000 scanner (Axon), the data collected using GenePix (ver. 5.0) software, and uploaded to our database for analysis (http://www.ou.edu/microarray). The data were normalized by a local Lowess algorithm (17) implemented on our database and the replicate arrays averaged for analysis. Clustering algorithms were implemented in Spotfire DecisionSite for Functional Genomics software. .
Time (min) A600 Timepoint 120 0.257 rpoS tp1 150 0.372 rpoS tp2 160 0.391 rpoS tp3 170 0.432 rpoS tp4 180 0.434 rpoS tp5 190 0.438 rpoS tp6 200 0.472 rpoS tp7 210 0.513 rpoS tp8 220 0.561 rpoS tp9 250 0.78 rpoS tp10 290 1.21 rpoS tp11 315 1.55 rpoS tp12 330 1.63 rpoS tp13Crp Mutant Diauxie Time (min) A600 Timepoint 0 0.054 none 60 0.078 none 120 0.098 none 180 0.134 none 210 0.168 none 240 0.216 none 250 0.24 crp tp2 300 0.319 none 315 0.353 none 330 0.378 none 345 0.415 none 360 0.455 none 375 0.503 none 390 0.532 none 405 0.56 crp tp5 420 0.568 crp tp6 450 0.56 crp tp7RelA Mutant Diauxie Time (min) A600 Timepoint 832 0.198 tp1 865 0.283 tp2 896 0.437 tp4 909 0.53 tp5 916 0.526 tp6 925 0.526 tp7 935 0.532 tp8 945 0.535 tp9 955 0.535 tp10 966 0.582 tp11 976 0.626 tp12 1007 0.772 none 1036 0.959 none 1067 1.278 none 1095 1.479 none 1125 1.509 none 1140 1.544 none 1325 1.38 none |
 |
 |
|
Copyright © 2009 The Board of Regents of the University of Oklahoma | Disclaimer OU Bioinformatics Core Facility @ Advanced Center for Genome Technology | Credits | updated: 2 Feb 2006 |